Marketing is not just about selling products; it’s about understanding and influencing human behavior. Marketers often employ psychological principles to tap into consumers’ subconscious minds, driving decisions and behaviors that ultimately lead to increased sales. By leveraging fundamental aspects of human psychology, marketers can create more effective campaigns that resonate deeply with their target audiences. Here are five powerful psychological principles used in marketing, explained in depth.
1. Scarcity Principle
- Explanation: The scarcity principle operates on the fear of missing out (FOMO). When people believe that an item is in short supply, their desire to own it increases. This is because scarce items are perceived as more valuable and desirable. Scarcity creates a sense of urgency, compelling customers to act quickly to avoid missing out.
- Why It Works: This psychological response is rooted in our evolutionary past where resources were limited, and securing scarce resources could mean survival. Psychologist Robert Cialdini, in his book Influence: The Psychology of Persuasion, discusses how scarcity drives value perception. The principle is based on the idea that people assign more value to opportunities that are less available, leading to a heightened desire to obtain these scarce items. In modern marketing, this translates to higher sales as customers rush to purchase items before they run out.
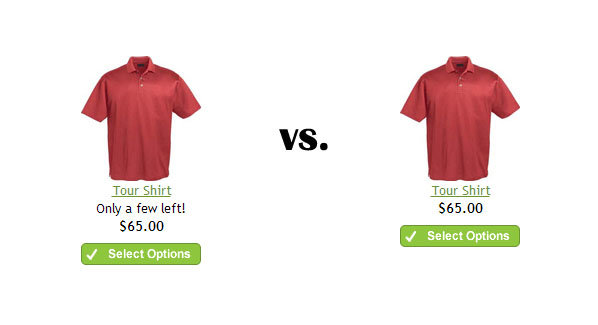

2. Social Proof
- Explanation: Social proof leverages the human tendency to conform to the actions of others, especially in situations of uncertainty. When people see others engaging in a behavior or endorsing a product, they are more likely to do the same. This includes user reviews, ratings, testimonials, and endorsements from celebrities or influencers.
- Why It Works: Humans are social creatures and often look to others for cues on how to behave. Social proof reduces the perceived risk of making a decision, as it suggests that many others have already made a successful choice. Social psychologist Robert Cialdini highlights the power of social proof in influencing behavior, noting that people are more likely to follow the actions of others, particularly in ambiguous situations. This principle helps build trust and credibility in marketing, encouraging potential customers to follow the crowd and make a purchase.

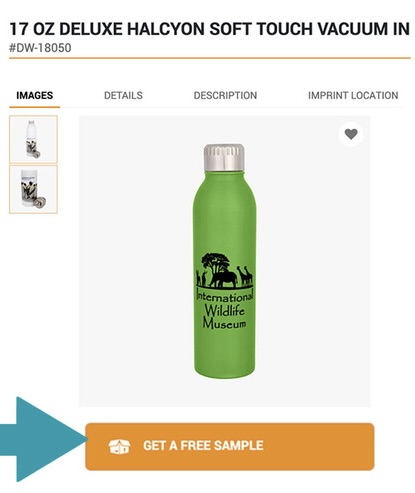
3. Reciprocity
- Explanation: The principle of reciprocity involves giving something of value to potential customers with the expectation that they will feel compelled to return the favor. This could be in the form of free samples, gifts, or exclusive content. The initial gesture creates a sense of obligation in the recipient.
- Why It Works: Reciprocity is a deeply ingrained social norm. When someone does something for us, we feel a natural urge to repay the favor. In marketing, this can lead to increased sales, as customers feel obliged to reciprocate the value they received. Psychologist Robert Cialdini explains that this principle works because people have a built-in desire to return favors, which helps build relationships and trust. By giving something of value first, marketers can trigger this response, leading to higher customer engagement and sales.
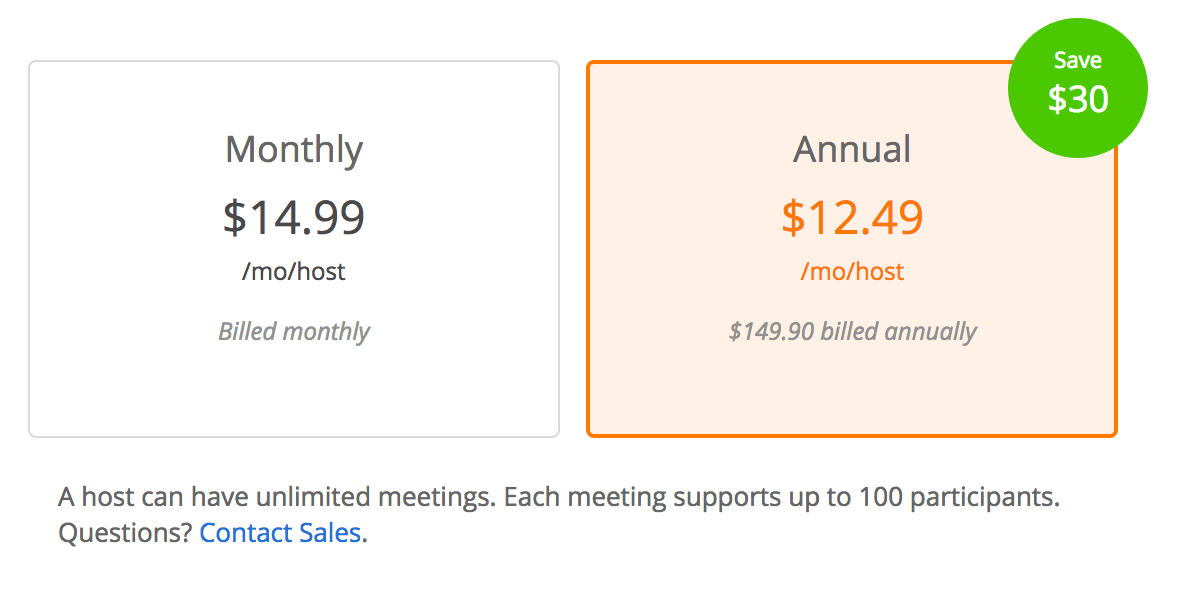
4. Anchoring
- Explanation: Anchoring occurs when people rely heavily on the first piece of information they encounter (the anchor) when making decisions. In pricing strategy, the initial price shown sets a reference point. Subsequent prices are then judged relative to this anchor. For example, displaying a high-priced item first makes other items appear more affordable in comparison.
- Why It Works: The anchoring effect is a cognitive bias that impacts decision-making and perception of value. It simplifies complex decisions by providing a reference point, making it easier for customers to evaluate options. This principle is extensively studied by psychologists Amos Tversky and Daniel Kahneman, who found that people rely too heavily on the first piece of information they receive when making decisions. In marketing, this means that presenting a higher price first can make subsequent prices seem more reasonable, leading to increased sales.
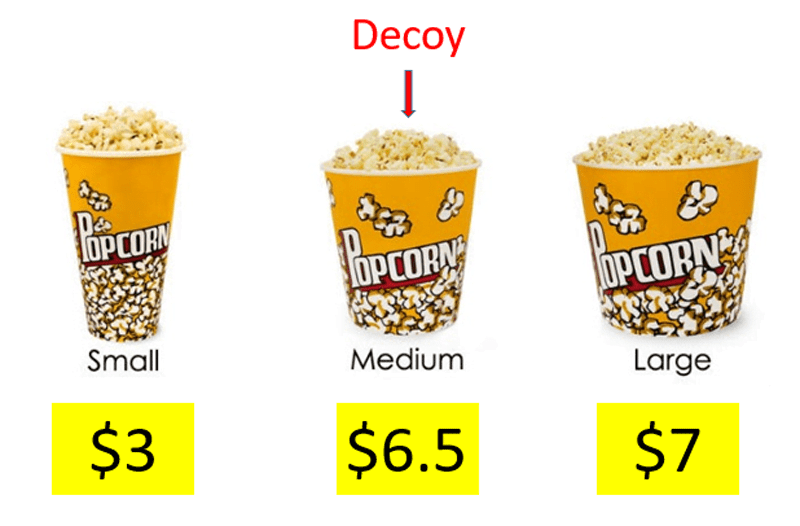
5. Decoy Effect
- Explanation: The decoy effect involves presenting a third option that is asymmetrically dominated by one of the other two options. This makes one of the options appear more attractive by comparison. For instance, if there are two subscription plans, adding a third, less attractive plan can steer customers towards the more profitable option.
- Why It Works: The decoy effect simplifies decision-making by making the superior choice appear obvious. It reduces the cognitive load on the customer, guiding them towards a decision that seems rational and beneficial. Behavioral economist Dan Ariely have explored how the introduction of a decoy option can influence choices. By adding a third option that makes one of the other options look more attractive, marketers can steer customers towards the option they want to promote, leading to higher sales and customer satisfaction.

Understanding the psychological principles behind marketing tactics can provide valuable insights into why we make certain purchasing decisions. Marketers use techniques like the scarcity principle, social proof, reciprocity, anchoring, and the decoy effect to subtly influence our behavior and drive sales. By being aware of these strategies, you can become a more informed consumer and make decisions that are truly in your best interest.
Can you now notice more of these tricks everywhere around you? Next time you see a limited-time offer or a glowing testimonial, take a moment to think about the psychological principles at play. Stay informed, and make smarter choices!
If you found this article insightful, share it with your friends and help them become savvy consumers too! For more fascinating insights into marketing psychology, subscribe to our newsletter and never miss an update.




Leave a comment